Global Root-zone moisture Analysis & Forecasting System (GRAFS)¶
Date modified: April 2022
Product Overview¶
Background¶
Root-zone soil moisture is a measure of water stored in the soil that is accessible to plant roots, making it a major contributing factor to plant health and crop yield.
The Global Root-zone moisture Analysis & Forecasting System (GRAFS) is produced by the ANU Centre for Water and Landscape Dynamics. The model estimates the surface (0-5 cm) and root-zone (0-1 m) soil moisture at 10 km spatial resolution globally, using the precipitation measured by the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission and through assimilation of the soil moisture product from the Soil Moisture Active/Passive (SMAP) mission.
This product is regularly updated and made available through National Computational Infrastructure’s open access THREDDS data server. The product base url is https://dapds00.nci.org.au/thredds/dodsC/ub8/global/GRAFS/.
For more information on this product, contact Luigi Renzullo and Siyuan Tian.
A Jupyter Notebook which demonstrates loading and using this dataset in the Sandbox is also available.
Specifications¶
Table 1: GRAFS product specifications
Specifications |
|
|---|---|
Product name |
Global Root-zone moisture Analysis and Forecasting System (GRAFS) |
Cell size - X (degree) |
0.1 |
Cell size - Y (degree) |
-0.1 |
Coordinate reference system |
EPSG:4326 |
Update frequency |
Daily |
Temporal extent |
2015 - present |
Processing¶
The Global Root-zone moisture Analysis and Forecasting System (GRAFS) is a near-real time data assimilation system that combines complementary information from model simulations and satellite observations to provide soil moisture estimates at near surface and root-zone. In GRAFS, satellite soil moisture observations from Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) are assimilated into a simple first-order autoregressive model that captures the soil moisture conditions in response to precipitation, namely, the Antecedent Precipitation Index (API) model. Satellite precipitation from Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) is used to drive the API model to simulate near surface soil moisture at 5cm. The assimilation of SMAP data relies on the four-dimensional variational (4DVAR) method to adjust the modelled surface soil moisture towards observations within a 4-day assimilation window. Soil Water Index (SWI) is then derived from the analysed surface soil moisture using an exponential filter and represents the root-zone soil wetness at approximate 1m depth. The surface and root-zone wetness from GRAFS can be converted into absolute soil moisture content using soil physical properties to provide essential support for a wide variety of hydrological and agricultural applications.
Media and example images¶
Figure 1: GRAFS surface soil moisture and rootzone soil moisture data for the Il Ngwesi region of Kenya from 01-07-2018 to 31-05-2019.
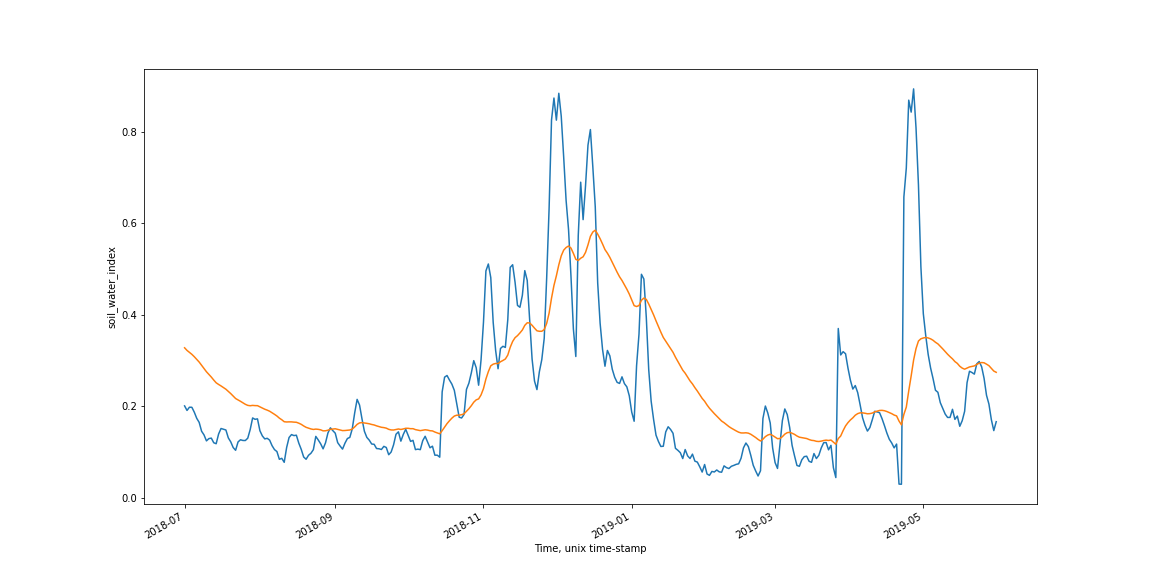
Credit: Contains surface soil moisture and rootzone soil moisture GRAFS data.
License¶
The Global Root-zone moisture Analysis and Forecasting System (GRAFS) product is provided under a Creative Commons 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License.
Data Access¶
The GRAFS dataset is external to the Digital Earth Africa Open Data Cube. Digital Earth Africa provides the load_soil_moisture() function in the Soil Moisture Notebook to enable users to access the data from the National Computational Infrastructure’s THREDDS OPeNDAP service. The Soil Moisture
Notebook shows how to query and load the dataset.